START
the Moon for a day the Moon for a year
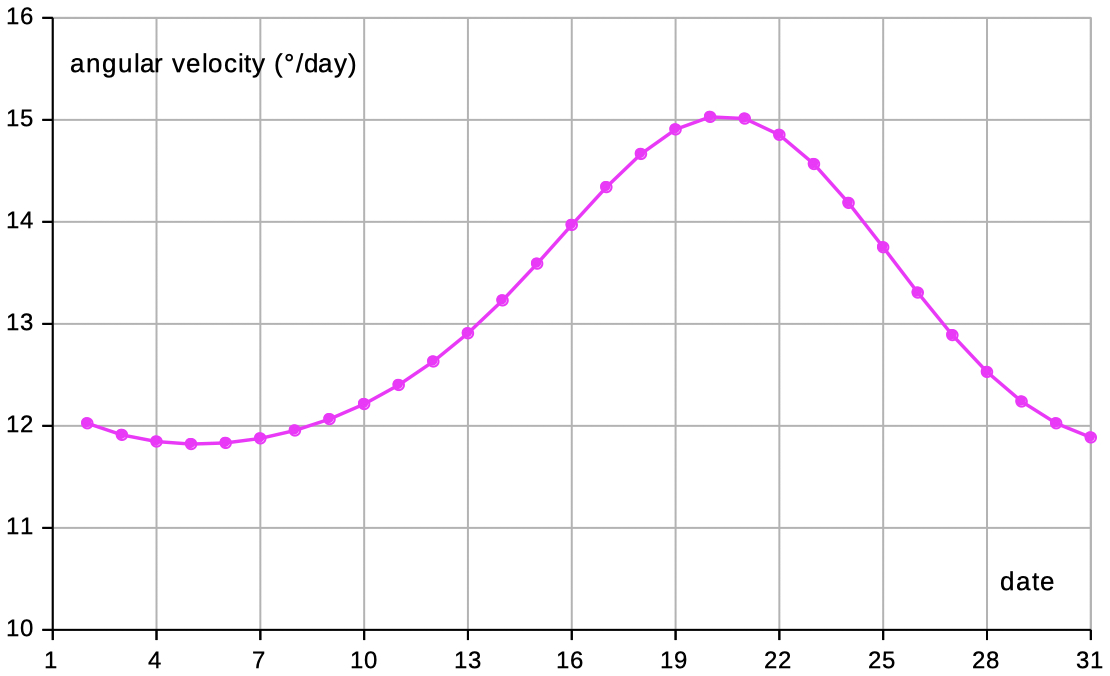
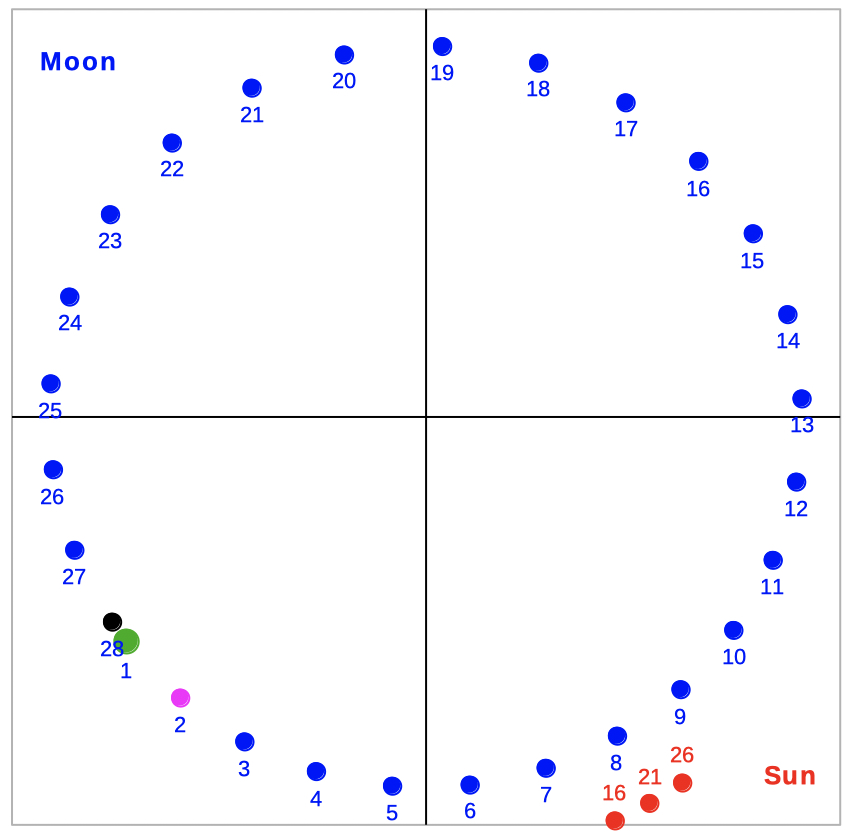
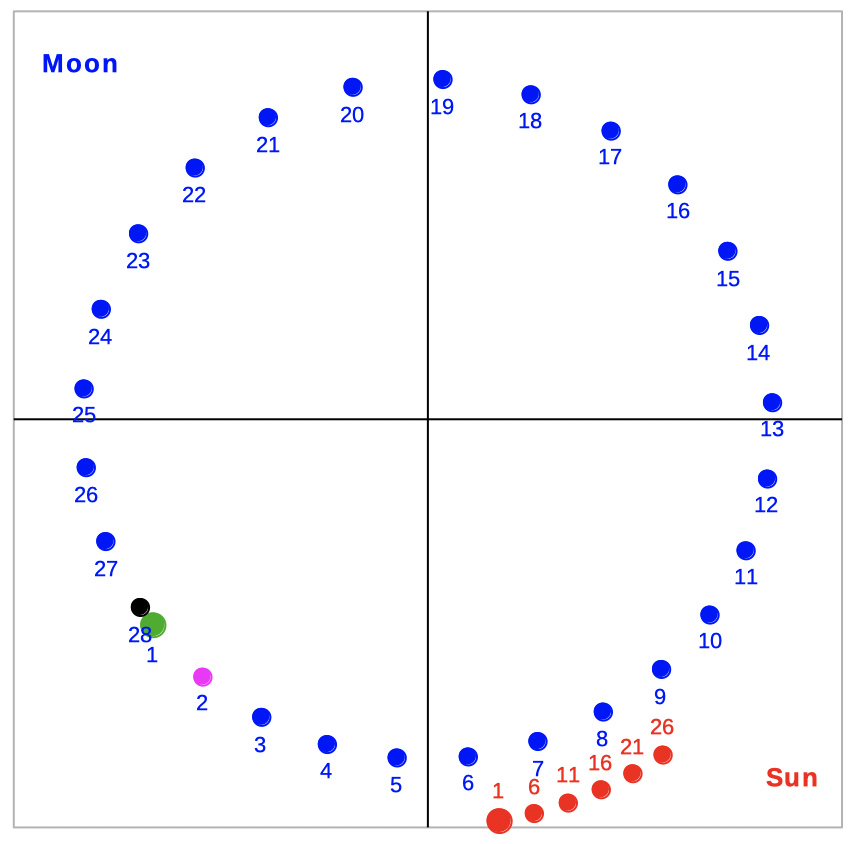
Position of the Moon by
Spreadsheet
for a month
download
| Select the table 'input': | |
|
Input (red frames): 1) hour UT, min |
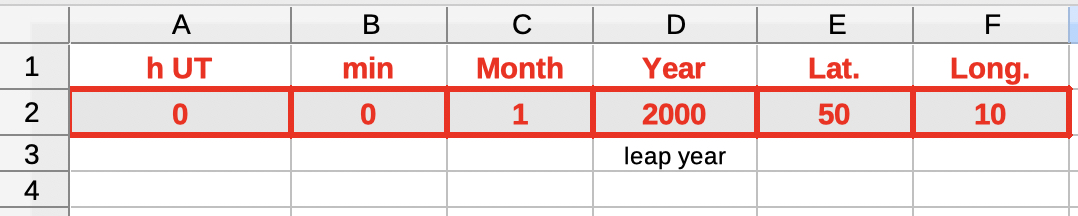 |
| The table 'calc' performs the calculations, using a lot of auxiliary variables. Don't edit any cell. | |
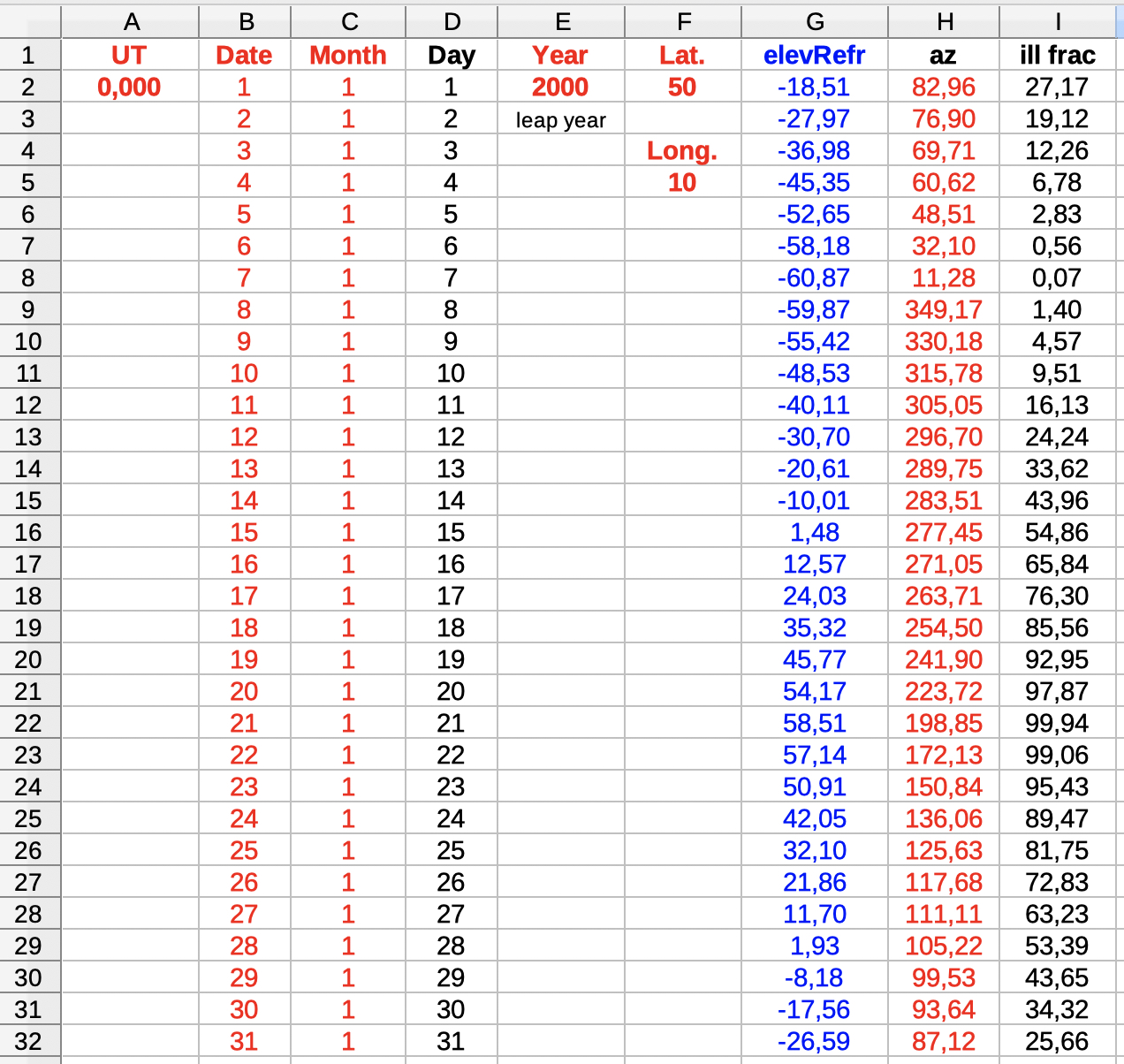
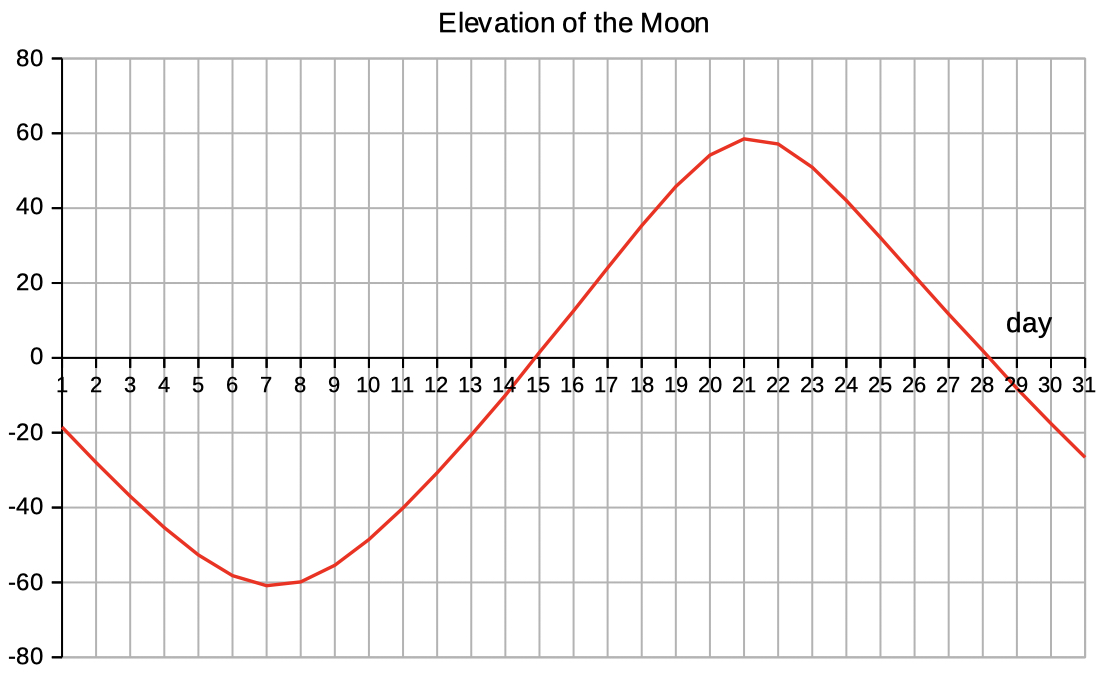
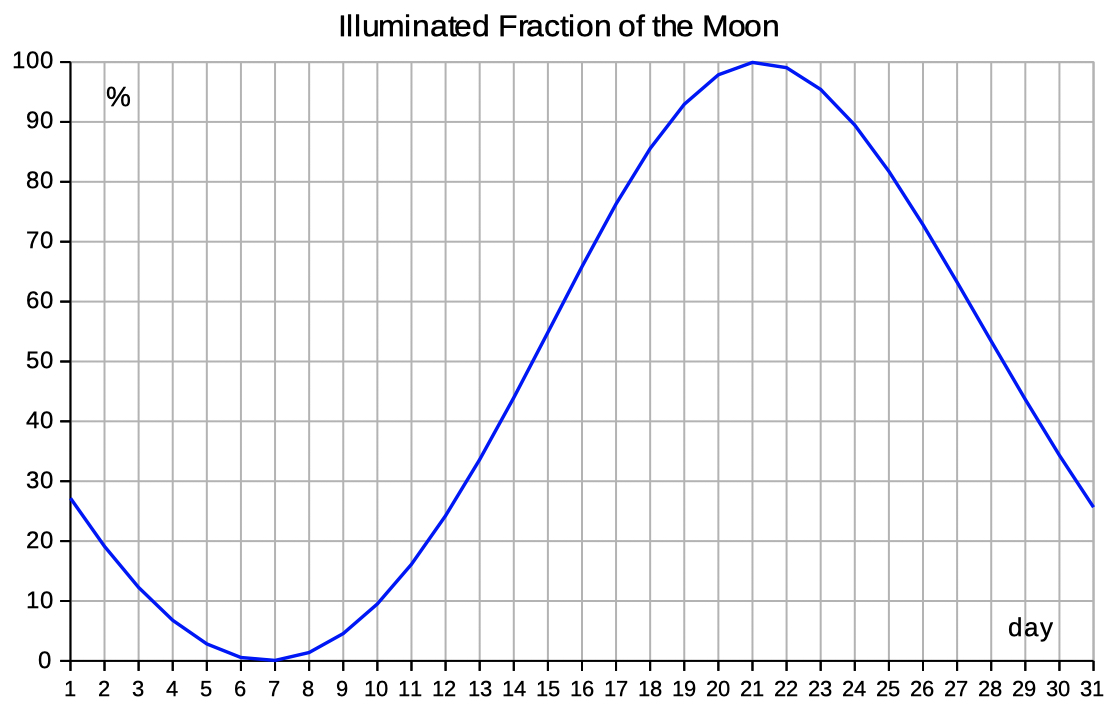
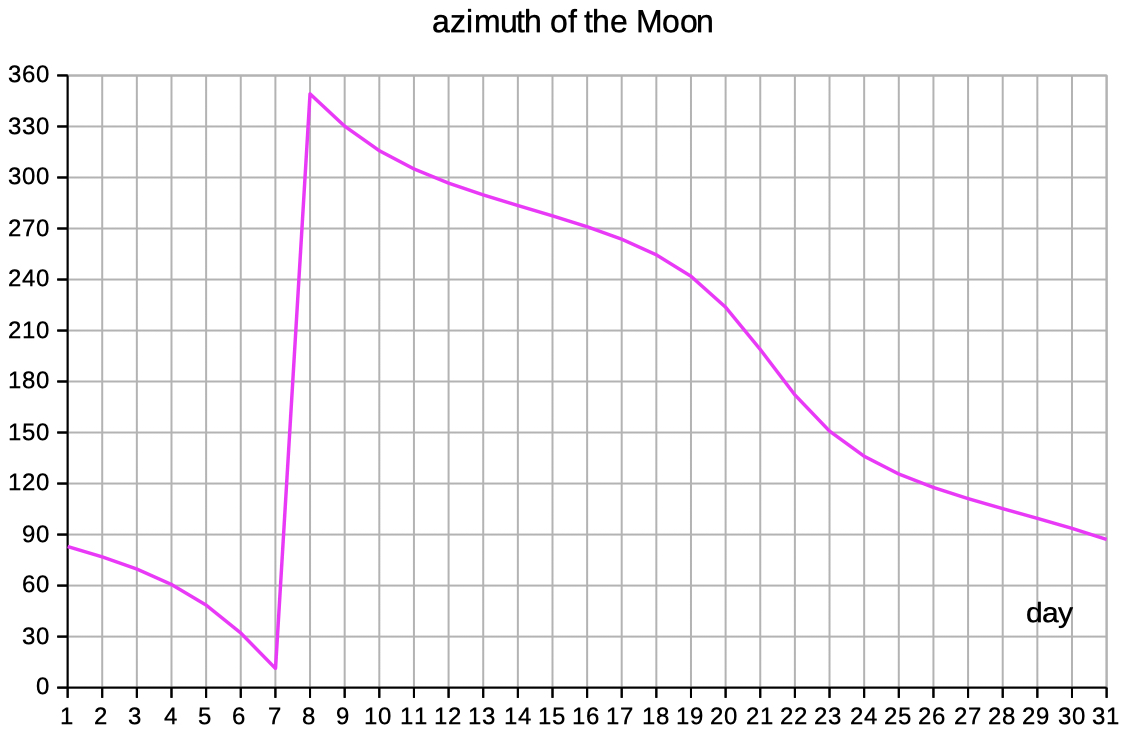
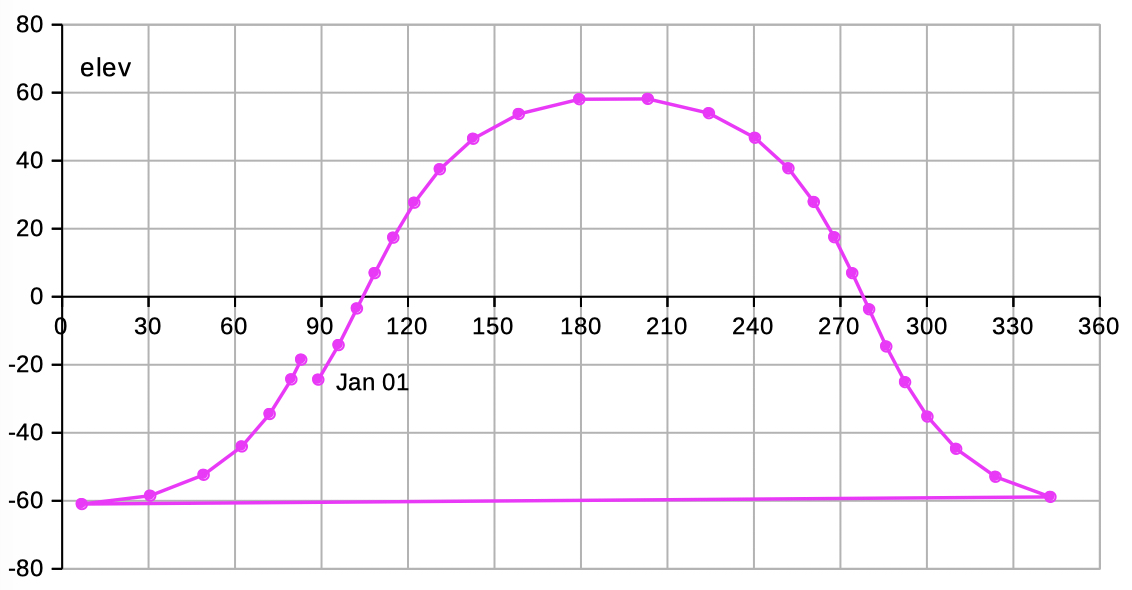
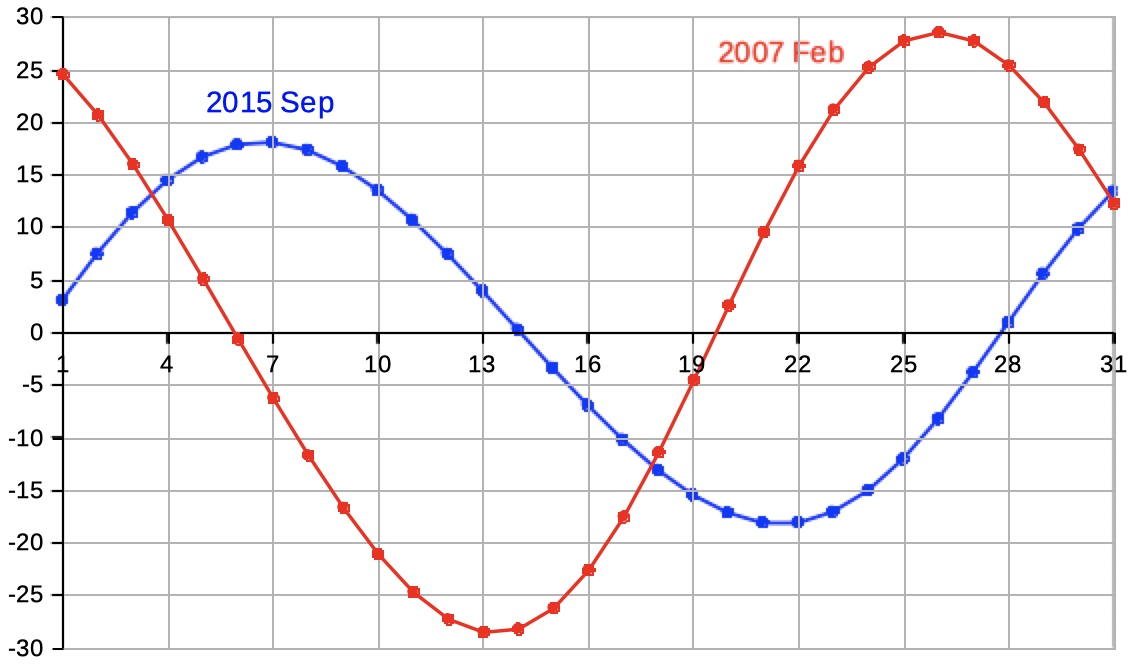
| Select 'elev az_illum' to see data and diagrams of elevation, azimut and illumination. | |
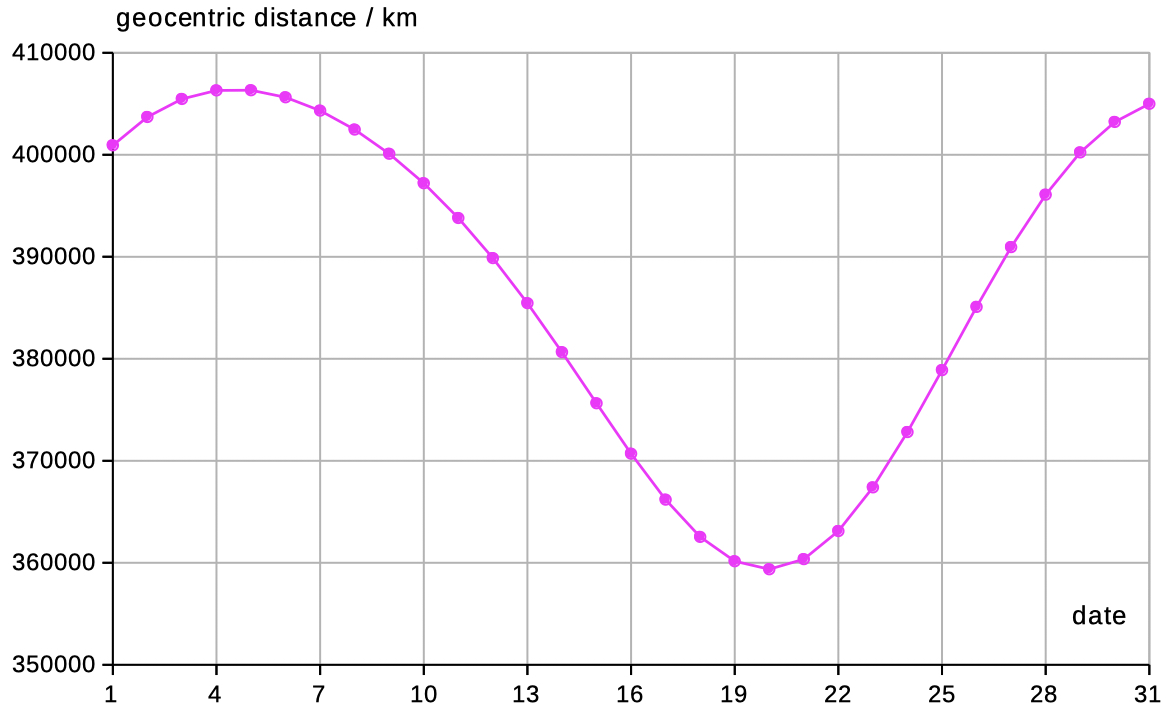
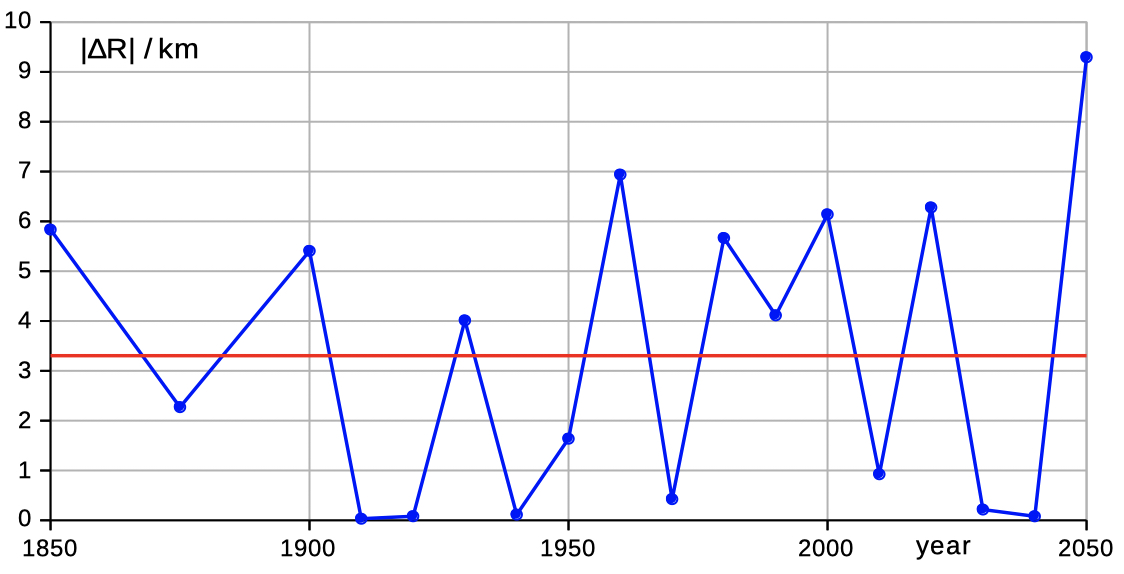
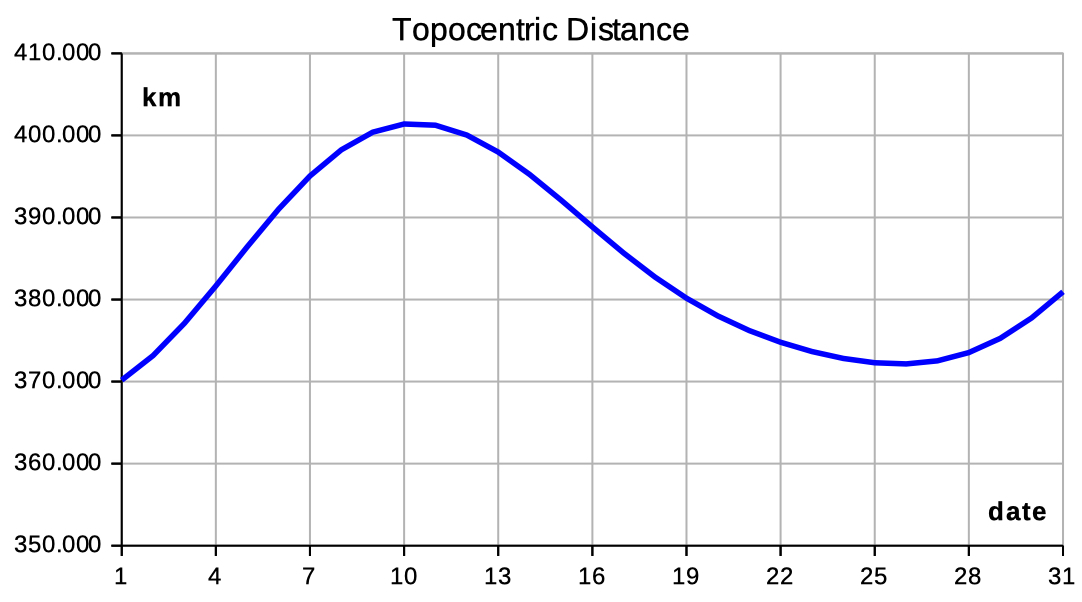
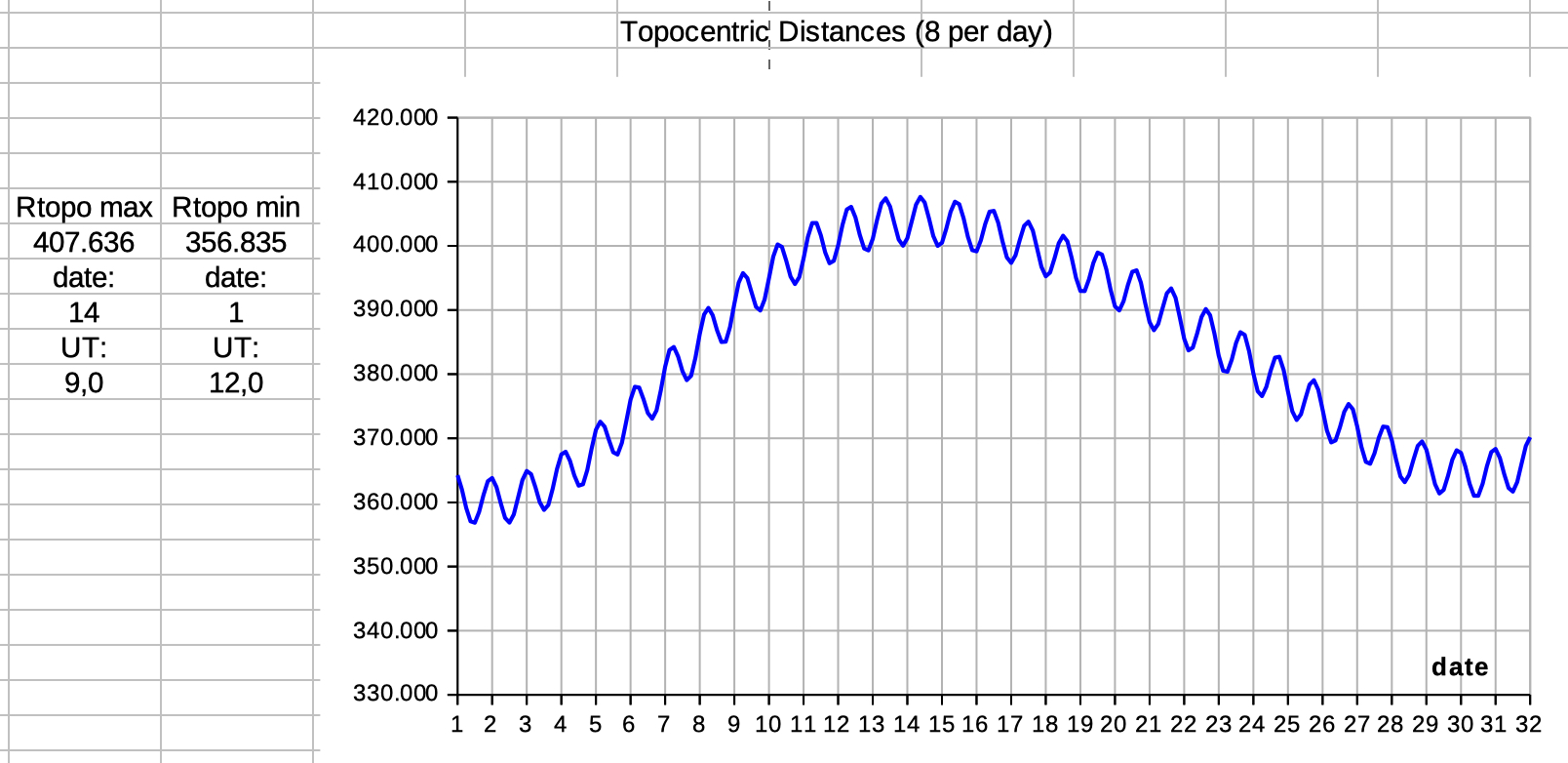
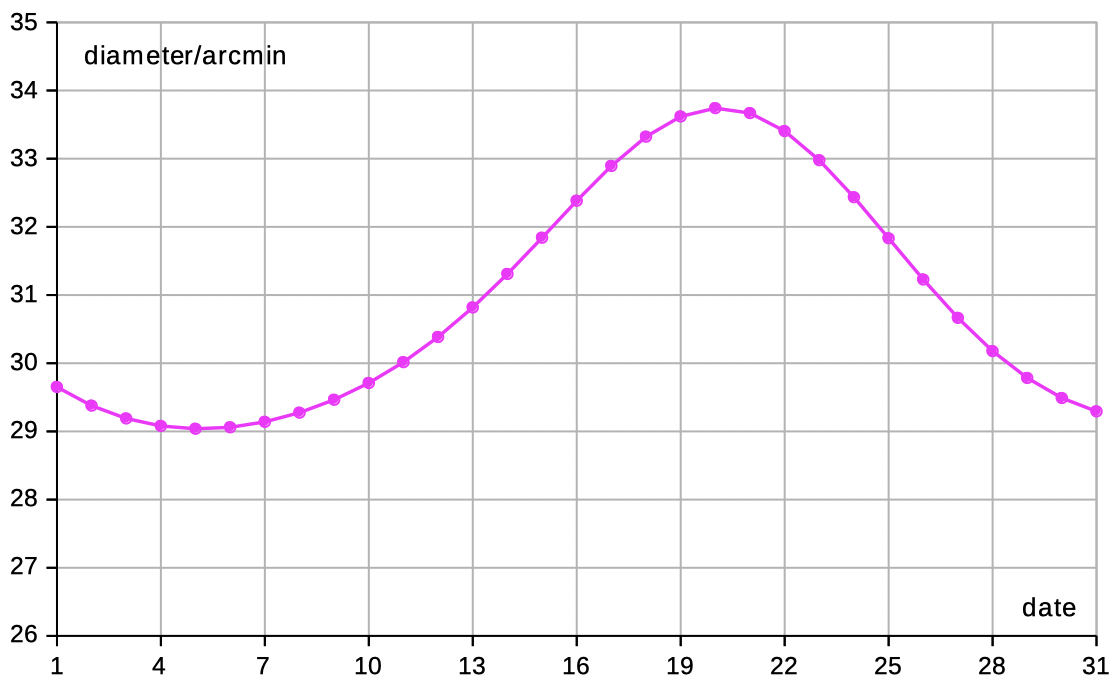
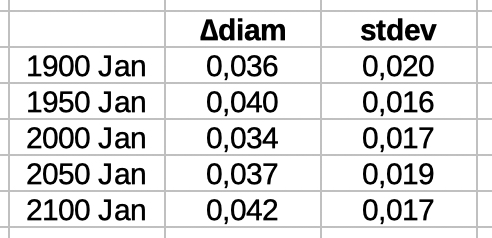
| Select 'distance declin' to see data and diagrams of geocentric distance and declination. | |
| Select 'orbit' to see the orbit of the Moon around the Earth. | |
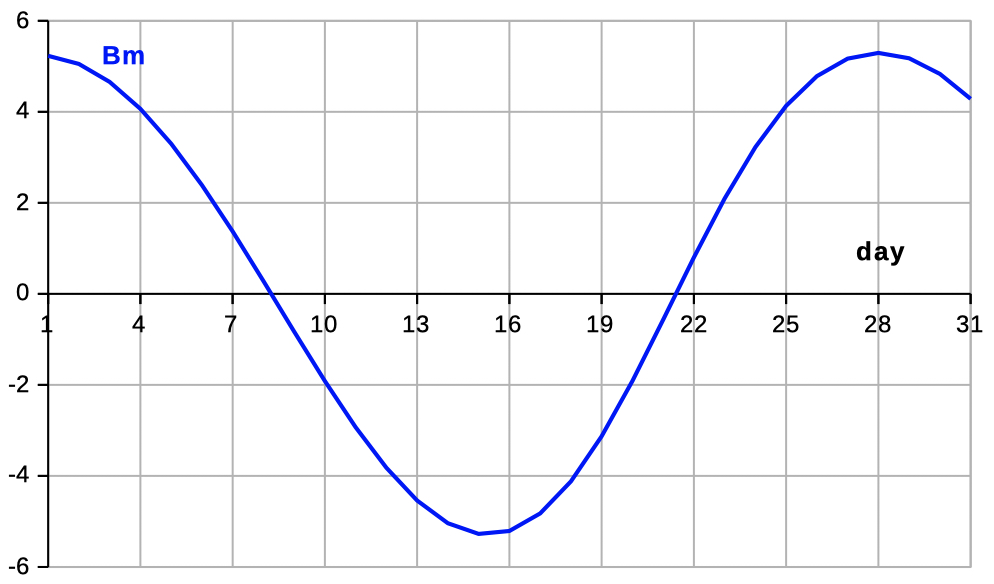
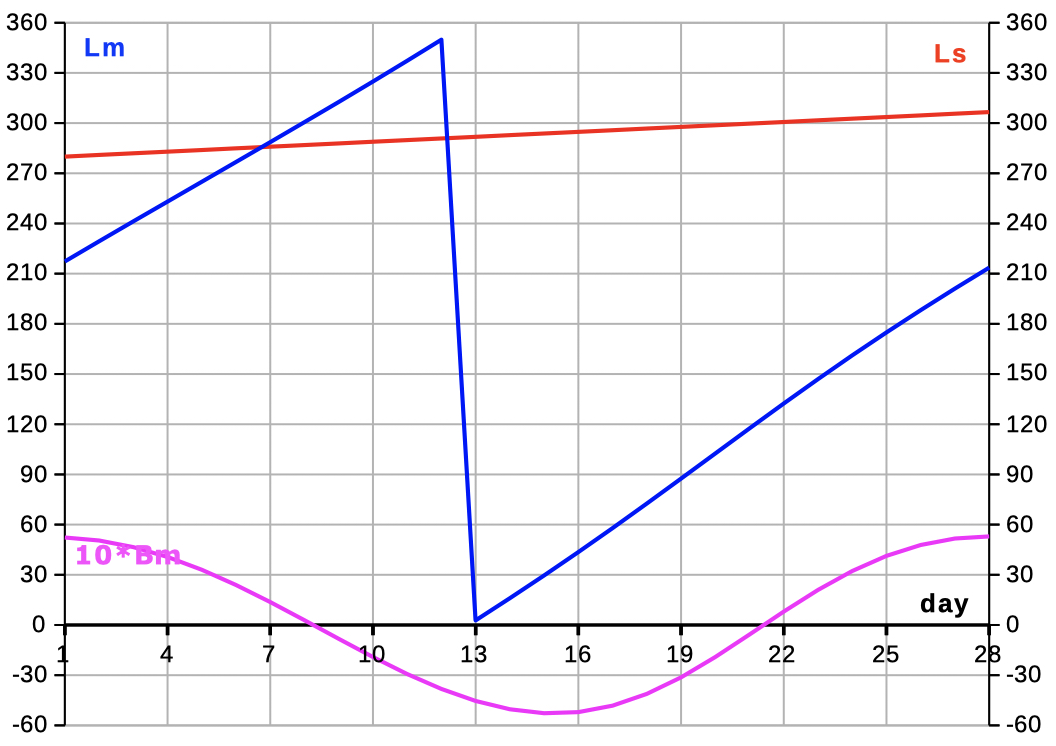
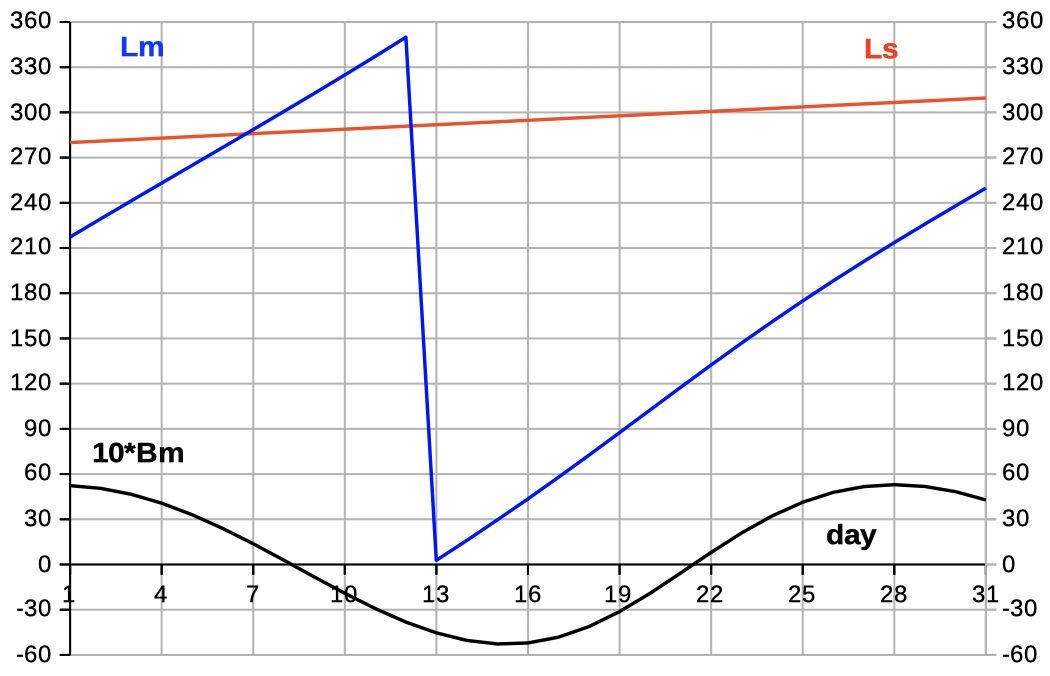
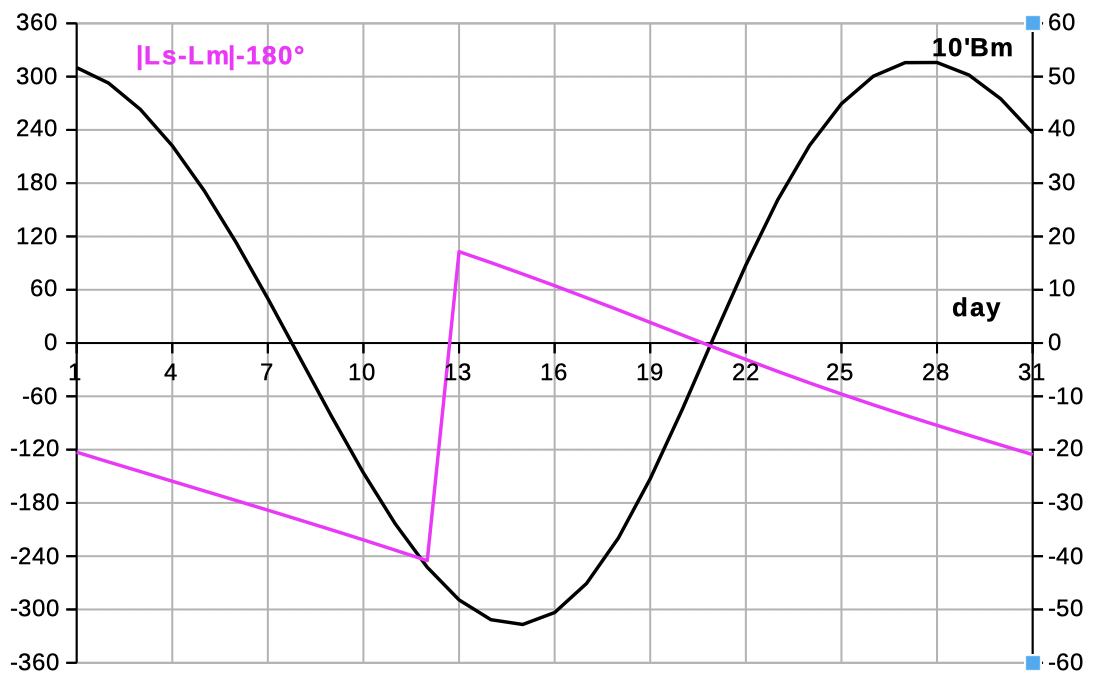
| Select 'L B' to see data and diagrams of ecliptic longitude and latitude. | |
| Select 'sol ecl' to explore solar eclipses. | |
| Select 'lun ecl' to explore lunar eclipses. |