|
|
GeoAstro Applets |
Chaos Game |
Java |
Miscel- laneous |
The Sun's Meridian Transit
    |
Enter latitude in decimal degrees, enter longitude in decimal degrees, |
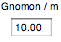  |
enter gnomon height (meters), |
 |
Use the keys "y", "m",
or "d" to increase the year, month, or day, or shift key and "y", "m", or "d" to decrease the year, month, or day. |
  |
Use the command key and
"u" or "d" to move up or down. Use "Reset" from the Details menu to reset the position and the zoom. |
  |
enter aperture diameter (in mm), |
 |
is the year 2009 |
 |
Select "Write Data" or "Write Table" from the Details menu to open data windows. |
The meridian in Basilica di Santa Maria degli Angeli e dei Martiri in Rome
The meridian in the Cathedral of Milan
The meridian of St. Sulpice in Paris
Meridian line sundials
were the earliest means of checking the accuracy of
calendars. A special form was developed in Italy during
the fifteenth century. Instead of using the shadow of an
obelisk, the sun was allowed to shine through the wall
or roof of a building onto a meridian line on the floor
inside, and the point of light was used as the
indicator.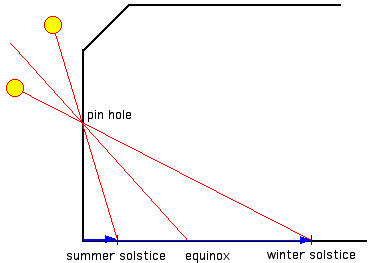 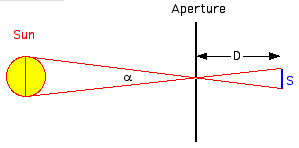 The diameter
S of the disk of light is mainly determined by the
apparent diameter α of the Sun:
S = D·tan α
The
diameter a of the aperture and an amount due to
diffraction (2·D·1.22·λ/a) has to be added
to S.
|
Meridian lines in churches
(adapted from M. Catamo, C. Lucarini):
| Year
of construction |
City | Church/Building | Height
of gnomon hole |
Constructor |
| 1467 | Florence | S.
Maria del Fiore |
90.11
m |
P. Toscanelli |
| 1636 | Marseille | College of Oratory | 17
m |
P. Gassendi |
| 1655 | Bologna | San
Petronio |
27.07
m |
G.
D. Cassini |
| 1702 | Rome | S.
Maria degli Angeli |
20.34
m |
F. Bianchini |
| 1743 | Paris | S.
Sulpice |
26
m |
Le
Monnier |
| 1786 | Milan | Cathedral | 23.82
m |
A.
De Cesaris, G. Reggio |
| 1791 | Naples | National Archaeol. Museum | 14
m |
G.
Cascella |
| 1841 | Catania | Monastery
S. Nicolol'Arena |
23.92
m |
C.
F. Peters, W. Sartorius |
| 1794 | Palermo | Cathedral | C11.78
m |
G.
Piazzi |
| 1895 | Modica | S.
Giorgio |
C14.18
m |
A.
Perini |
|
|
|
Santa Maria degli
Angeli e dei Martiri (Wikipedia) A Guide to “The Sun in the Church” by
J. L. Heilbron L'Almanacco Astronomico - La vostra eclisse |
| Books |
| J. L.
Heilbron: The Sun in the Cathedral, Cathedrals as
Solar Observatories, Harvard University Press, 1999. Marco Catamo, Cesare Lucarini: Il Cielo in Basilica. La Meridiana delle Basilica di Santa Maria degli Angeli e dei Martiri in Roma, A.R.P.A. Edizioni AGAMI, Roma 2002. |

Updated: 2023, Oct 06